Tubular heating elements
Due to the range of shaping options, tubular heating elements (heating rods) provide a variable and affordable solution for a wide range of applications. The most frequently used diameters of heating rods are ø 6.5 mm, ø 8.5 mm.
We also offer: ø 5.2 mm, ø 10.5 mm, ø 12.5 mm, ø 15.5 mm, and ø 16.5 mm.
Specification
Wattage tolerance:
- +5%/-10% above 200 W of the nominal wattage (measured at working temperature).
- +10%/-10% up to 25 W – 200 W of the nominal input power (measured at working temperature).
Tolerance of the diameter of heating rods: +/-0.05 mm in case of ø 6.5 and ø 8.5 mm, +/-0,2 mm offer diameters
Recommended operating voltage:
- rods ø 6.5 mm 12 V – 250 V (maximum 400 V).
- rods ø 8.5 mm 12 V – 480 V (maximum 600 V).
Maximum amperage
- rods ø 6.5 mm 15 A
- rods ø 8.5 mm 30 A
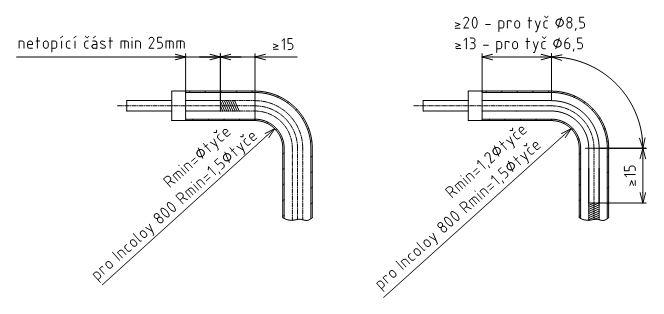
Length of no-heating ends: min. 25 mm (cannot be used for every type of electrotechnical terminations)
The shell material and the recommended watt density of the heating rods (W/cm2) is stated according to the working conditions of the element (see Heating gases, liquids, and solid substances).
Materials used for the sheath: AISI 304, AISI 309, AISI 321, AISI 316L, AISI 316Ti, ALLOY 825, INCOLOY 800, steel 11 353, copper.
In the case of the application for heating air, there is the option of winding the rod with a stainless strip to increase the area of the heat passage into the space and to increase the service life of the rod or the maximum recommended value of the watt density of the rod for specific working conditions (see Heating gases).
If the client will shape the heating rods, the minimum recommended diameter of bending is 38 mm, for rods ø 6.5 mm and 50 mm, for rods with a diameter of 8.5 mm (these values do not apply to rods from material Incoloy800). N.B. Once shaped, the rod must not be straightened back. After shaping, the rod must be retested for the electrical strength of the insulation and the electric circuit according to ČSN EN 60335-1.
For more information or in the case of other parameters than those mentioned above, please contact us.
Construction limits
Standard methods for cementing tubular elements
Polyurethane sealant (up to 135 °C) – is used for elements with a low working temperature, e.g. for heating water.
Epoxy resin (up to 146 °C) – reports higher mechanical resistance compared with polyurethane sealants.
High chemical resistance to acids and alkalis.
Silicone sealant (guaranteed up to 275 °C) – elements for air. Not suitable for applications requiring increased resistance to moisture.
High temperature epoxy resin – air and liquids up to 250 °C.
High chemical resistance to acids and alkalis.
Ceramic sealant (up to 1,500 °C) – applications with high working temperatures. Not suitable for applications requiring increased resistance to moisture.